Comprehensive Guide to EMI Shielding Materials
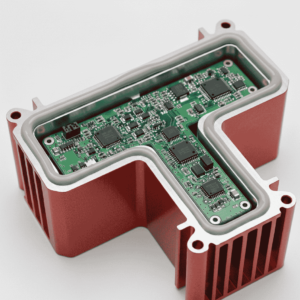
Protecting sensitive electronics from electromagnetic interference is critical for modern device reliability. By properly categorizing shielding materials, engineers can effectively block unwanted signals and prevent cross-talk between internal components. High-quality EMI shielding materials are essential for meeting regulatory standards and ensuring clear signal integrity in wireless applications.
Key Categories of EMI Shielding Materials
To help you select the right protection, we categorize our materials based on their physical properties and shielding performance:
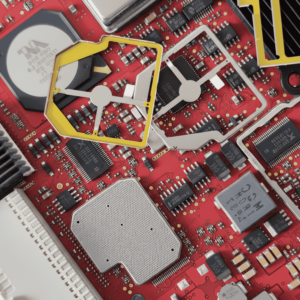
- Conductive Elastomers: These materials combine silicone with conductive fillers like silver-plated aluminum or nickel-graphite. They provide both environmental sealing and excellent electromagnetic protection.
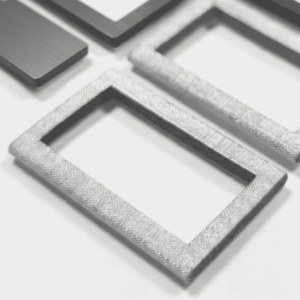
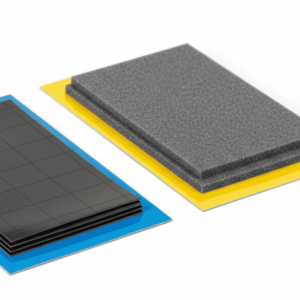
- Fabric-over-Foam Gaskets: Ideal for commercial applications, these materials offer high flexibility and low compression set. They are perfect for shielding enclosure doors and seams where a soft touch is required.
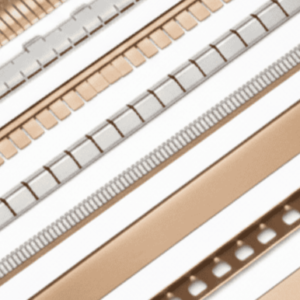
- Metal Foils and Tapes: For quick fixes or high-frequency grounding, copper and aluminum shielding materials provide a low-impedance path to ground and are easy to apply via adhesive backings.
- Conductive Coatings and Thin Films: These are specialized materials applied directly to plastic housings, providing a lightweight barrier for mobile devices and handheld electronics.
Why Shielding Effectiveness Matters
The primary metric for shielding effectiveness is decibel (dB) attenuation. When selecting a material, it is vital to match the attenuation levels to the specific frequency range of your interference. For instance, high-frequency $5G$ applications require different EMI shielding materials compared to low-frequency industrial power equipment.
Installation and Compliance of EMI shielding materials
Using the correct shielding materials is only half the battle; proper grounding and contact resistance are equally important. For technical validation, you can refer to international testing standards such as IEEE 299 to verify the performance of your chosen shield. By understanding these categories, you ensure your product remains compliant and free from electronic noise.